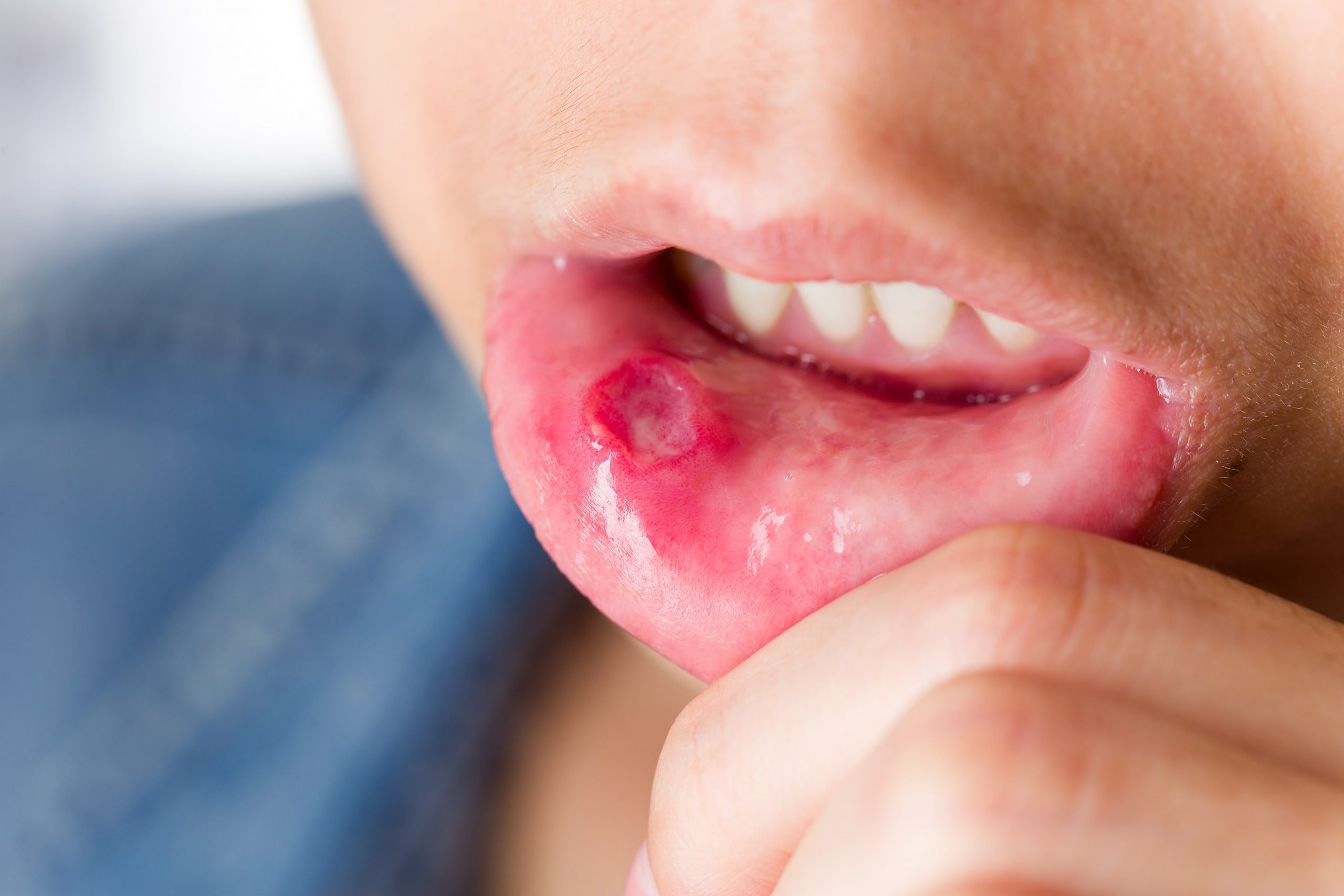
These are small, painful lesions in your mouth or at the base of the gums. They’re also called canker sores. People with mouth ulcers have difficulty eating, drinking or speaking.
Teenagers, women and those with a family history of mouth ulcers have greater chances of getting infected.
One cannot transmit mouth ulcers – they typically disappear in a week or two. But for large or very painful and persistent mouth ulcers, see your healthcare provider.
Book an AppointmentThis condition has no particular cause. Certain things make it happen, including:
There are other chronic underlying health conditions that can be symptomised by mouth ulcers. They include:
Canker sores are of three types:
Contact your doctor when you experience:
By physically examining your mouth, the sores can be identified. Where the mouth ulcers are frequent and chronic, testing for other health issues may be done.
These sores don’t require any treatment. But where you have severe mouth ulcers from time to time, here are some treatments that can lower pain: